Explaining about cloud computing and its advantages
Cloud computing is a technology paradigm that involves the delivery of computing services, including servers, software, analytics, and more.
In today's fast-paced digital world, cloud computing has emerged as a revolutionary technology that has transformed the way individuals and businesses manage and access their data and applications.
The concept of cloud computing has gained immense popularity due to its scalability, cost-efficiency, and convenience. In this blog post, we will delve deep into the world of cloud computing, exploring its fundamental concepts, architecture, and the myriad advantages it offers to both individuals and organizations.
What is Cloud Computing?
At its core, cloud computing is a technology that allows users to access and use computing resources (such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, and analytics) over the internet, often referred to as "the cloud."
These resources are hosted and maintained by cloud service providers, and users can leverage them on a pay-as-you-go basis, scaling up or down as needed. In essence, cloud computing eliminates the need for organizations and individuals to own and manage their physical hardware and software infrastructure, making it an attractive option for various computing needs.
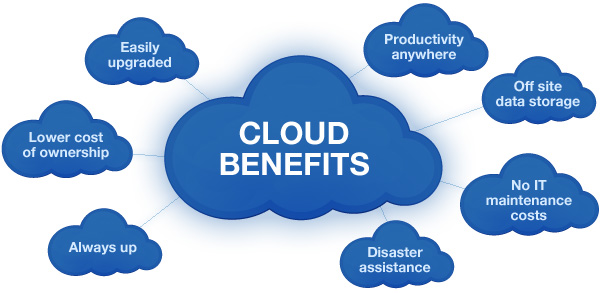
Advantages of Cloud Computing
- Cost-Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of cloud computing is its cost-efficiency. Traditional IT setups require substantial investments in hardware, software, and maintenance. In contrast, cloud computing offers a pay-as-you-go model, where users only pay for the resources they use. This reduces upfront capital expenses and allows businesses to allocate their budgets more efficiently. Additionally, cloud providers benefit from economies of scale, which often result in lower costs for their customers.
- Scalability
Scalability is another key benefit of cloud computing. Whether you're a startup experiencing rapid growth or an established enterprise, cloud resources can easily scale up or down to match your requirements. This elasticity allows you to respond quickly to changing demands without the need for significant infrastructure investments or downtime.
- Flexibility and Accessibility
Cloud computing provides unparalleled flexibility and accessibility. Users can access their data and applications from anywhere with an internet connection, using various devices, including smartphones, tablets, and laptops. This flexibility enables remote work, collaboration across geographies, and easy access to critical business tools.
- Reliability and Redundancy
Leading cloud providers invest heavily in data center infrastructure to ensure high availability and reliability. They typically offer Service Level Agreements (SLAs) that guarantee a certain level of uptime, often exceeding what most organizations can achieve with on-premises infrastructure. Moreover, data redundancy and backup options are readily available in the cloud, reducing the risk of data loss due to hardware failures or disasters.
- Security
Cloud providers prioritize security and compliance to protect their customers' data. They employ dedicated teams of security experts, employ advanced encryption techniques, and implement multi-factor authentication to safeguard sensitive information. In many cases, cloud providers offer a more secure environment than what individual organizations can achieve on their own.
- Automatic Updates and Maintenance
Cloud providers handle the maintenance and updates of the underlying infrastructure and software. This means users no longer need to worry about patch management, hardware upgrades, or system maintenance, allowing them to focus on their core business activities.
- Resource Optimization
Cloud computing allows for efficient resource allocation. Users can scale resources up or down based on demand, which means they never overpay for idle capacity. This optimizes resource utilization and ultimately reduces costs.
Types of Cloud Computing
There are several deployment models and service models in cloud computing:
- Deployment Models:a. Public Cloud: Resources are owned and operated by a third-party cloud service provider and are made available to the general public. Examples include AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform.b. Private Cloud: Resources are dedicated to a single organization and can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider. Private clouds offer greater control and customization but may be more expensive.c. Hybrid Cloud: A combination of public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to be shared between them. Hybrid clouds offer flexibility and can be used to optimize costs and compliance.d. Community Cloud: Shared by several organizations with common interests, such as regulatory requirements or security concerns. It offers benefits of both public and private clouds while addressing specific community needs.
- Service Models:a. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS): Provides virtualized computing resources over the internet, including virtual machines, storage, and networking. Users have control over the operating system and applications but not the underlying infrastructure.b. Platform as a Service (PaaS): Offers a platform with tools and services for application development and deployment. Users can focus on coding and not worry about managing infrastructure or runtime environments.c. Software as a Service (SaaS): Delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. Users can access and use software without the need for installation or maintenance. Examples include Google Workspace and Microsoft 365.d. Function as a Service (FaaS): Also known as serverless computing, FaaS allows developers to run individual functions or pieces of code in response to events without managing servers. It offers great scalability and cost savings for event-driven applications.
Real-World Applications of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has become the backbone of many modern technologies and applications, driving innovation across various industries. Here are some real-world examples:
- E-commerce: Online retailers use cloud computing to handle spikes in web traffic during peak shopping seasons, ensuring a seamless shopping experience for customers.
- Healthcare: Cloud computing enables healthcare providers to securely store and share patient records, conduct remote consultations, and analyze medical data for research and diagnostics.
- Education: Educational institutions leverage cloud platforms for online learning, virtual classrooms, and collaborative tools, especially in remote or hybrid learning environments.
- Entertainment: Streaming platforms like Netflix and Spotify rely on cloud infrastructure to deliver content to millions of users worldwide, ensuring high-quality streaming and personalization.
- Finance: Banks and financial institutions use cloud computing for risk analysis, fraud detection, and customer service while adhering to strict security and compliance standards.
- Manufacturing: Cloud-based IoT (Internet of Things) platforms help manufacturers monitor equipment, predict maintenance needs, and optimize production processes.
- Gaming: Cloud gaming services like Google Stadia and NVIDIA GeForce NOW enable gamers to play high-end games on low-end devices by offloading the processing to cloud servers.
Challenges and Considerations
While cloud computing offers numerous advantages, there are also challenges and considerations to keep in mind:
- Security and Compliance: Storing data in the cloud can raise security concerns, especially for sensitive information. Organizations must carefully choose cloud providers with strong security measures and ensure compliance with relevant regulations.
- Data Transfer Costs: Transferring large volumes of data to and from the cloud can incur additional costs. It's essential to understand the pricing structure of the chosen cloud provider.
- Downtime: Despite high availability guarantees, cloud services can experience outages. Organizations should have contingency plans in place to minimize the impact of downtime.
- Vendor Lock-In: Moving data and applications between cloud providers can be challenging, leading to vendor lock-in. Careful consideration of long-term strategies is essential.
- Data Sovereignty: Some industries and countries have regulations that require data to remain within specific geographic boundaries. Ensure that the chosen cloud provider can meet data sovereignty requirements.
Cloud computing has revolutionized the way we access, store, and manage data and applications. Its advantages, including cost-efficiency, scalability, flexibility, and security, have made it an indispensable technology for individuals and organizations across various industries.
Whether you're a startup, a large enterprise, or an individual user, the cloud offers a multitude of benefits that can propel your digital endeavors to new heights. Embracing the cloud is not just an option; it's a necessity for staying competitive and agile in the modern era of computing.
What's Your Reaction?
















